The Main Applications for Switches
A network switch has many applications. Switches:
- Can be used to manage the flow of data across a network
- Can be linked together to handle medium to large LANs.
- Are often used in a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) application, which usually employs a single switch to access a variety of bandwidth services
- Are used to connect network devices physically
- Can transfer data to other devices using the half-duplex or full-duplex mode
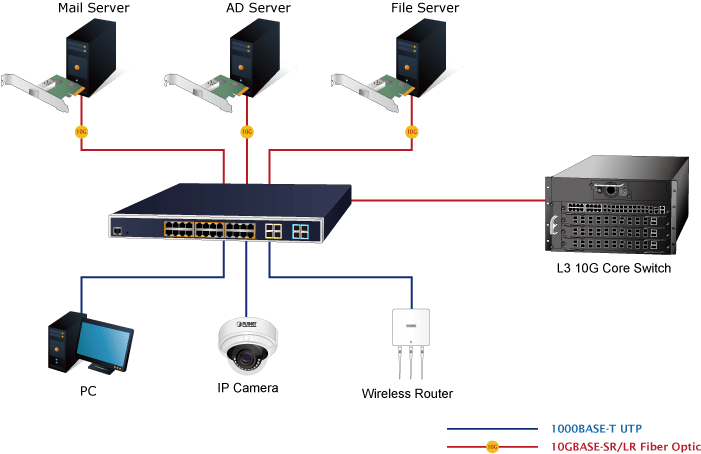
The Main Applications for Routers
Here are eight ways to use a router. A router:
- Can create a LAN
- Allows the splitting of the internet connection to all network devices
- Can connect different media and devices
- Can be used to run a firewall
- Can be used to determine where to send data from one computer to another
- Can perform Packet Forwarding, Switching, and filtering
- Makes sure that data reaches its intended destination
- Can connect to a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
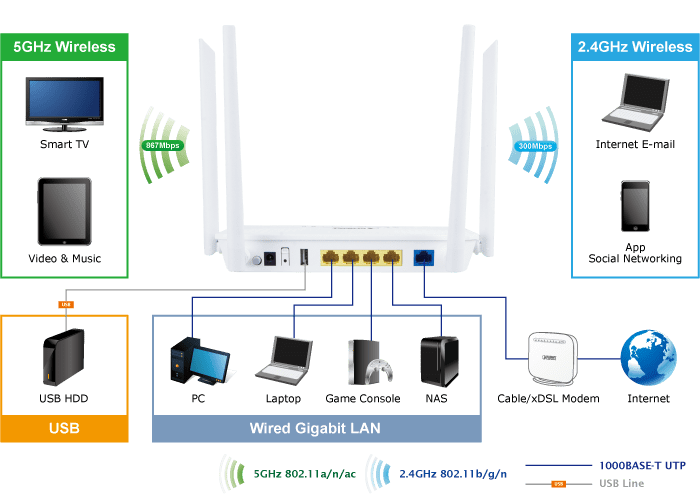
As with any type of equipment, there are advantages and disadvantages to using either a switch or a router.
The Pros and Cons of the Network Switch
Pros
- The use of a switch reduces the number of broadcast domains. A large amount of broadcast traffic can negatively impact a network, so reducing broadcast domains is worth considering.
- Switches support VLANs which help in logical segmentation (commonly referred to as VLAN communication). Logical segmentation provides notable benefits in LAN administration, security, and management.
- Switches use the Content Addressable Memory (CAM) table for Port-to-MAC mapping.
Cons
- Switches are not as good as routers when it comes to limiting broadcast.
- Switches require inter-VLAN routing to enable communication between VLANs. However, it is important to note that there are many multilayer switches available these days.
- When handling multicast packets, switches require some configuration and proper design.
The Pros and Cons of the Router
Pros
- Routers deliver data packets in an organized way, which helps decrease data load.
- Routers offer stable and reliable connections between network hosts.
- If a central part fails to transfer data packets, routers have alternative ways to make the transfer happen.
Cons
- When multiple computers are using the network at the same time, router connections can slow down. This situation is referred to as “connection wait.”
- Since routers thoroughly analyze from the physical to the network layer (instead of just reading two layers of information), the connection can become slow.
- Routers typically require a lot of initial configuration and Network Address Translation (NAT), making set up a bit complicated.
 HANSUN
HANSUN 